Fiber deprivation and microbiome-borne curli shift gut bacterial populations and accelerate disease in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease - ScienceDirect
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 13 maio 2024

Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by motor dysfunction, dopaminergic neuron loss, and alpha-synuclein (αSyn) inclusion…

Parkinson's disease: Are gut microbes involved? American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology

Implications of the Human Gut–Brain and Gut–Cancer Axes for Future Nanomedicine

Dietary fibre deprivation and bacterial curli exposure shift gut microbiome and exacerbate Parkinson's disease-like pathologies in an alpha-synuclein-overexpressing mouse

Dietary fibre deprivation and bacterial curli exposure shift gut microbiome and exacerbate Parkinson's disease-like pathologies in an alpha-synuclein-overexpressing mouse

Implications of the Human Gut–Brain and Gut–Cancer Axes for Future Nanomedicine

Fiber deprivation and microbiome-borne curli shift gut bacterial populations and accelerate disease in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease - ScienceDirect

Novel compound FLZ alleviates rotenone-induced PD mouse model by suppressing TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway through microbiota–gut–brain axis - ScienceDirect

Implications of the Human Gut–Brain and Gut–Cancer Axes for Future Nanomedicine
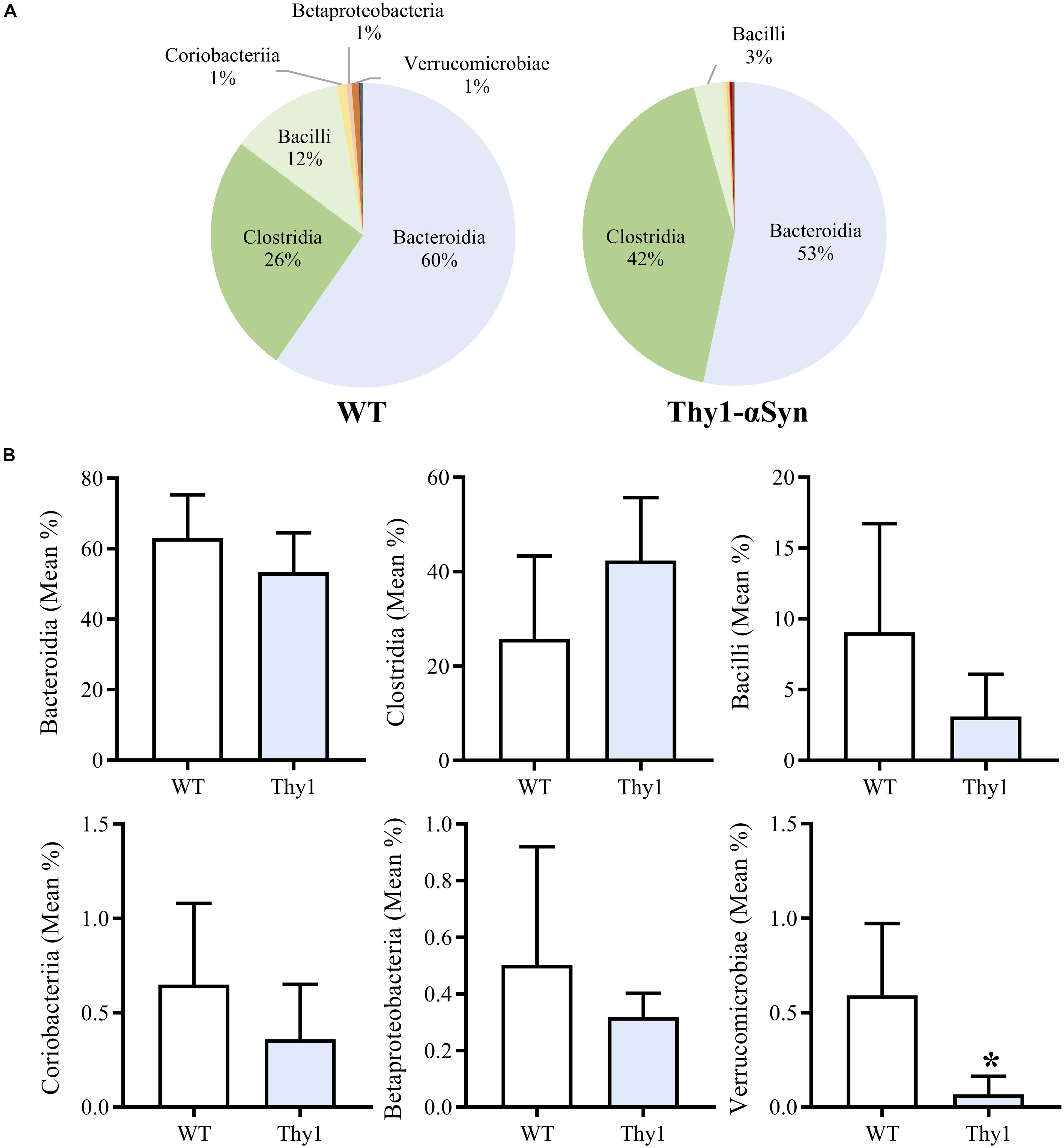
Frontiers Altered Gut Microbiome in Parkinson's Disease and the Influence of Lipopolysaccharide in a Human α-Synuclein Over-Expressing Mouse Model

Beneficial reconstitution of gut microbiota and control of alpha-synuclein and curli-amyloids-producing enterobacteria, by beta 1,3-1,6 glucans in a clinical pilot study of autism and potentials in neurodegenerative diseases

Gut Microbiota Regulate Motor Deficits and Neuroinflammation in a Model of Parkinson's Disease - ScienceDirect

Emerging insights between gut microbiome dysbiosis and Parkinson's disease: Pathogenic and clinical relevance - ScienceDirect

Fiber deprivation and microbiome-borne curli shift gut bacterial populations and accelerate disease in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease - ScienceDirect
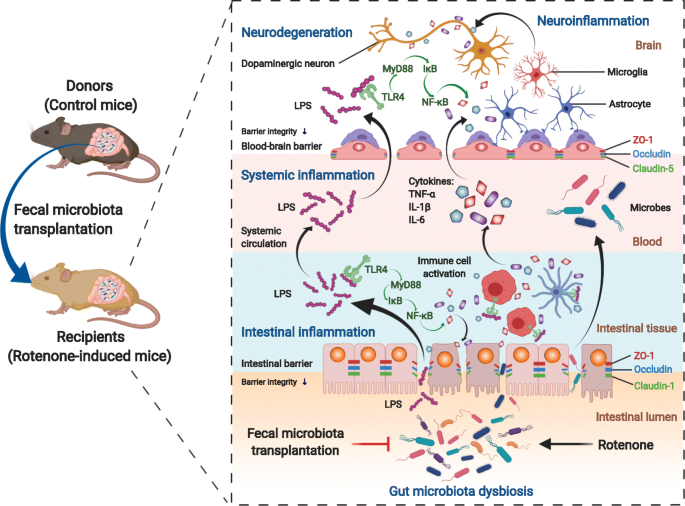
Fecal microbiota transplantation protects rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease mice via suppressing inflammation mediated by the lipopolysaccharide-TLR4 signaling pathway through the microbiota-gut-brain axis, Microbiome
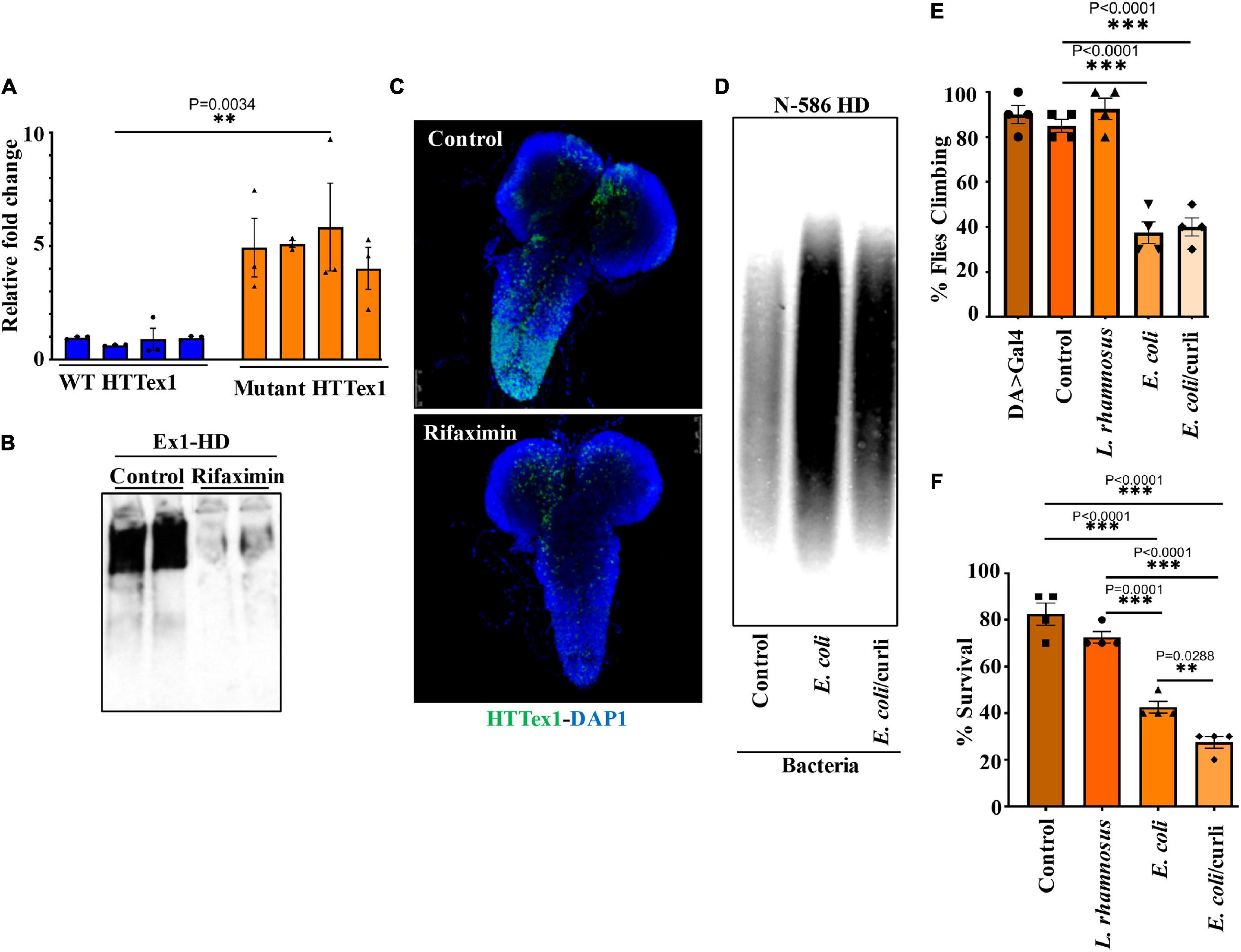
Frontiers Gut Bacteria Regulate the Pathogenesis of Huntington's Disease in Drosophila Model
Recomendado para você
-
 Como jogar GTA RP no PC – Tecnoblog13 maio 2024
Como jogar GTA RP no PC – Tecnoblog13 maio 2024 -
dudà games (@_dudagames) / X13 maio 2024
-
Twitch13 maio 2024
-
SOLTEIRA E GADA. Iris gta rp!, gta rp!, By DUDÀ GAMES13 maio 2024
-
 duda games gta rp13 maio 2024
duda games gta rp13 maio 2024 -
 GUGU E DUDA TRETARAM FEIO, QUEM TAVA CERTO ? 👀😱😤13 maio 2024
GUGU E DUDA TRETARAM FEIO, QUEM TAVA CERTO ? 👀😱😤13 maio 2024 -
 COLOMBIA NA FUGA DE MOTO X DUDA UMA DAS MELHORES GTM / GTAV RP / CIDADE ALTA13 maio 2024
COLOMBIA NA FUGA DE MOTO X DUDA UMA DAS MELHORES GTM / GTAV RP / CIDADE ALTA13 maio 2024 -
beijo da duda games|Pesquisa do TikTok13 maio 2024
-
melhores momentos gta rp, gta, By DUDÀ GAMES13 maio 2024
-
 ENCONTREI A DUDA NO ROLEPLAY MOBILE - SÓ OS GADOS - One State RP13 maio 2024
ENCONTREI A DUDA NO ROLEPLAY MOBILE - SÓ OS GADOS - One State RP13 maio 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Sun Spot Outfit With Hair - Subway Surfers by HammerBro101 on DeviantArt13 maio 2024
Sun Spot Outfit With Hair - Subway Surfers by HammerBro101 on DeviantArt13 maio 2024 -
 Auction Prices Realized Tcg Cards 2017 Pokemon SM Black Star Promo HO-Oh GX MYSTERIOUS POWER TINS13 maio 2024
Auction Prices Realized Tcg Cards 2017 Pokemon SM Black Star Promo HO-Oh GX MYSTERIOUS POWER TINS13 maio 2024 -
 Human Cartoon Character Funny Expression Emotion Face Mouth Smirk Coffee Mug by Noirty Designs - Pixels13 maio 2024
Human Cartoon Character Funny Expression Emotion Face Mouth Smirk Coffee Mug by Noirty Designs - Pixels13 maio 2024 -
 Pokemon Gameboy Red, Green, Blue, Yellow, Silver, Gold, Crystal for Sale in Huntingtn Sta, NY - OfferUp13 maio 2024
Pokemon Gameboy Red, Green, Blue, Yellow, Silver, Gold, Crystal for Sale in Huntingtn Sta, NY - OfferUp13 maio 2024 -
 28 ideias de Capivarinha em 2023 capivara, capivaras, capivara desenho13 maio 2024
28 ideias de Capivarinha em 2023 capivara, capivaras, capivara desenho13 maio 2024 -
 Stream User 307948514 Listen to Gochuumon wa usagi desu ka playlist online for free on SoundCloud13 maio 2024
Stream User 307948514 Listen to Gochuumon wa usagi desu ka playlist online for free on SoundCloud13 maio 2024 -
 10ª Corrida de Natal de Blumenau finaliza com a participação de13 maio 2024
10ª Corrida de Natal de Blumenau finaliza com a participação de13 maio 2024 -
 Skins, Minecraft Bedrock Wiki13 maio 2024
Skins, Minecraft Bedrock Wiki13 maio 2024 -
 Old school gunplay with a remix --- Gun Crazy Review — GAMINGTREND13 maio 2024
Old school gunplay with a remix --- Gun Crazy Review — GAMINGTREND13 maio 2024 -
 Leagues Cup 2023: The reasons for MLS' dominance over Liga MX in13 maio 2024
Leagues Cup 2023: The reasons for MLS' dominance over Liga MX in13 maio 2024



